A new McKinsey report on AI and GenAI states that 65% of organizations use AI/GenAI extensively and derive business value from technology. Expectations from AI remain high, with predictions of significant and disruptive changes across industries in the coming years.
The life sciences industry, which initially lagged in AI adoption, has significantly caught up in recent quarters and is leveraging this technology within the GxP environment. AI applications and operations directly impact patient safety, product quality and data integrity.
Leveraging AI technology presents more than a technical challenge in the life sciences industry. The term “validation” has different connotations within AI/ML and the life sciences industry.
To illustrate, consider a scenario in which a biopharma client implements a new AI-driven system for its manufacturing process. While integrating AI, they realized they needed to conduct validation when integrating with their GxP systems. This realization raised apprehensions about AI validation and good automated manufacturing practice 5 (GAMP 5) validation, prompting questions about whether they were the same and which teams would be responsible for these activities. Additionally, they recognized the need for an AI framework to ensure transparency, ethics and trustworthiness in AI system outputs.
The life sciences industry requires AI/ML and GAMP 5 validation
In AI/ML, “validation” refers to evaluating model performance after a single training cycle, during which hyperparameters are tuned. Conversely, within life sciences, “validation” is a process of establishing documentary evidence to demonstrate that a GxP system performs its intended use with a high degree of probability.
Misinterpretations of the term “validation” in client interactions can overcomplicate the application of this technology in a regulated industry.
Understanding the relevance of GAMP 5 validation for AI/ML systems
GxP applications are subject to regulatory audits, making GAMP 5 particularly pertinent for AI systems integrated into GxP operations. This process emphasizes system lifecycle management, including designing, developing and testing AI systems to ensure data integrity, risk mitigation and compliance.
According to the International Society for Pharmaceutical Engineering’s GAMP 5, there are similarities in best practices between AI and traditional application development. Successful AI implementation requires thorough business analysis, effective planning and the application of good software development, engineering and maintenance practices. Data management must be implemented during the concept phase, as data is the key resource required to progress.
The process flow and table below highlight the distinct validation activities involved in AI/ML and provide insights into the various teams involved and how responsibilities are shared between the client, hyperscalers and service providers.
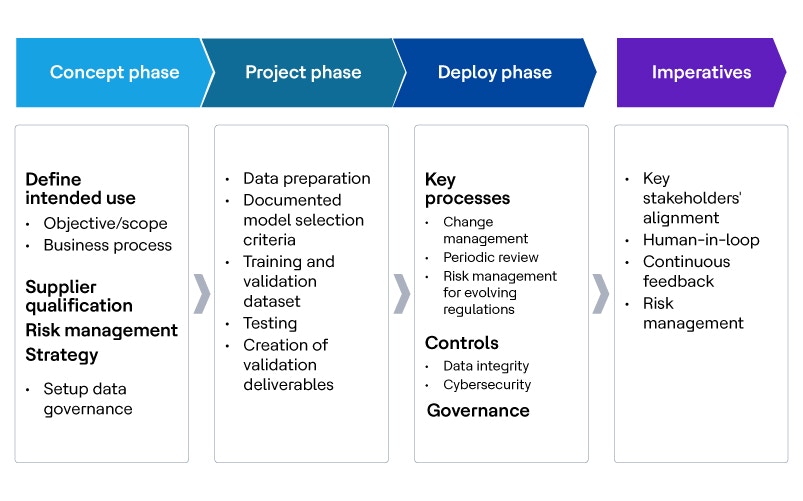
Validation types within the AI framework
| Validation type (phase) | Team responsible | Purpose | Key considerations |
| Data validation (concept phase) | Data scientist and process owner | To ensure data quality, integrity and accuracy of the datasets used for training and evaluating the AI applications |
|
| Model validation (project phase) | Hyperscalers | To ensure the accuracy of the model |
|
| Algorithm validation (project phase) | Hyperscalers | To ensure algorithms are functioning correctly, producing expected outcomes |
|
| API validation (project phase) | Development, quality and validation teams | To secure the AI systems from cyber threats and data breaches |
|
| Infra and application (project phase) | Development, quality and validation teams | Infrastructure, applications and interfaces are validated |
|
| Performance validation (deploy phase) | Business owner, process owner and service provider | To assess the AI model's performance |
|
AI validation and GAMP 5 validation focus on ensuring systems' reliability, safety and compliance by identifying and mitigating risks, validating systems throughout their lifecycle and providing transparent and traceable documentation.
Conclusion
Integrating AI/ML systems within the life sciences industry presents opportunities and challenges. The distinct interpretations of “validation” in AI/ML and GxP contexts necessitate a clear understanding and careful application of validation processes. GAMP 5 validation remains crucial for ensuring the reliability, safety and compliance of AI systems in regulated environments. By adhering to best practices and leveraging comprehensive validation frameworks, organizations can harness the potential of AI while maintaining the highest standards of quality and integrity.
As AI scales across clinical, manufacturing and supply chain use cases, clarity in validation will define leaders in life sciences. With domain expertise and partnerships with leading hyperscalers such as AWS, Microsoft, Google and more, we help life sciences firms deploy AI with confidence and compliance built in.
References
AI and Life Sciences Data Fusion | HCLTech




