The global MedTech market is on a strong growth trajectory, projected to reach $549,513.5 million by 2025 and $853,377.7 million by 2035. However, 30% of product delays are linked to compliance gaps (FDA), underscoring the critical role of regulatory adherence in accelerating innovation.
Against this backdrop, the newly published ISO 10993-1:2025 standard is more than a regulatory update — it’s a strategic imperative for manufacturers aiming to accelerate innovation while ensuring patient safety.
Navigating regulatory complexity
Regulatory complexity remains one of the biggest hurdles for MedTech companies. Failure to adapt quickly can result in significant consequences, including expensive recalls, slower approvals and missed market opportunities. ISO 10993-1:2025 demands a lifecycle-based, risk-managed approach, requiring organizations to rethink compliance strategies from design to disposal.
What’s changing? Key updates at a glance
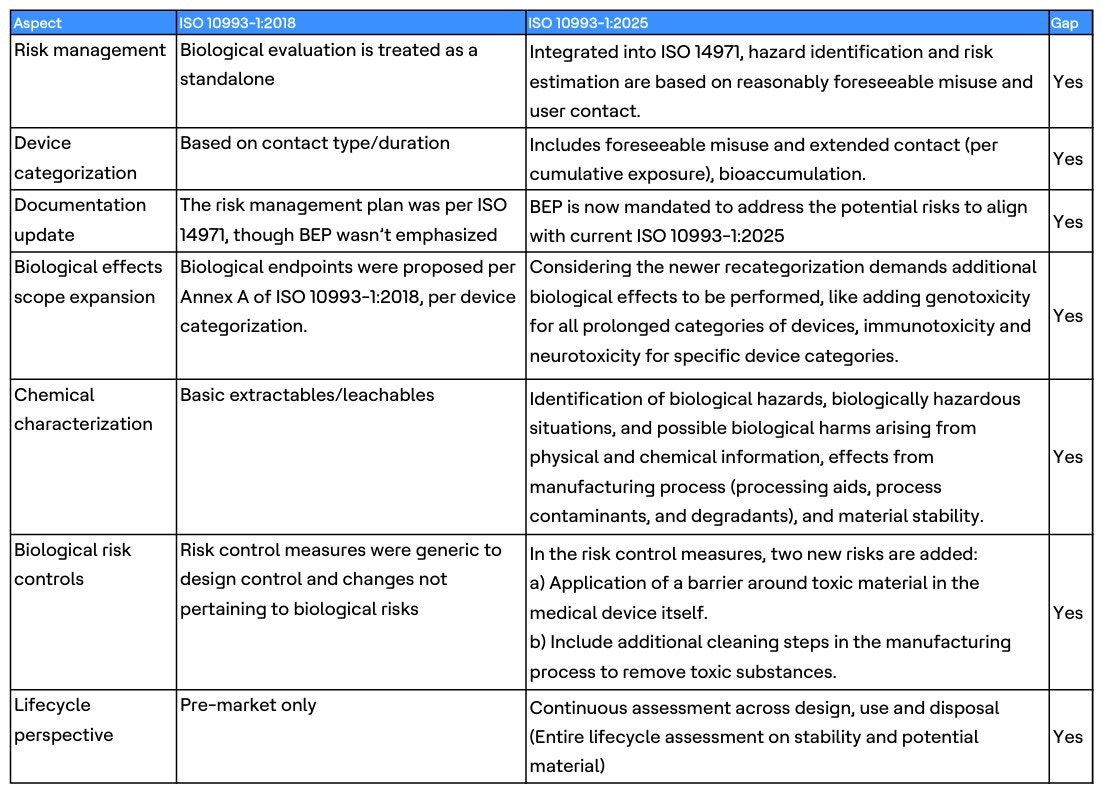
ISO 10993-1:2025 reframes biological evaluation, so it’s embedded in risk management and real-world use. Key themes to watch:
Real-world impact
The global biocompatibility testing market is valued at $3.13 billion in 2024 (projected to grow at a 9.3% CAGR through 2032), reflecting the rising importance and cost of robust testing frameworks. Medical device recalls in the US climbed nearly 9% in 2024 over 2023, reaching 1,059 events — signifying rising compliance risks and costs.
What does this mean for different devices?
ISO 10993-1:2025 changes are not one-size-fits-all. They impact device categories differently:
- Lancets and surgical tools: Previously low risk, now require testing, rationale, justification and documentation updates for extended contact scenarios
- Skin staples and endoscopic devices: Reclassified due to prolonged contact and foreseeable misuse, triggering additional biological effects and degradation studies
- Blood-contact devices: Long-term exposure demands systemic toxicity and bioaccumulation assessments
Why this matters for MedTech leaders
- Faster approvals: Early adoption reduces regulatory delays
- Cost optimization: Risk-based evaluations minimize unnecessary testing
- Portfolio protection: Timely updates prevent audits, delays and recalls
How HCLTech supported a MedTech firm in strengthening compliance amid ISO 10993‑1:2025 changes
A global minimally invasive surgery device manufacturer identified biological safety evidence gaps across more than 40 legacy Class II products as the updated ISO 10993-1:2025 standard raised expectations for deeper chemical characterization and long-term toxicological justification. Through our Materials CoE, we guided a structured portfolio review, including mapping materials, contact scenarios and risk categories, to identify where updated testing or robust scientific justification would be needed under the new standard.
We then supported the firm in realigning its biological evaluation strategy with ISO 10993-1, 10993-17, 10993‑18 and ISO 14971, modernizing chemical characterization and strengthening toxicological reasoning using up-to-date analytical and in‑vitro evidence. This enabled the company to refresh its biological safety documentation without disrupting global submissions and establish a stronger, future-ready framework for navigating ongoing regulatory changes.
At HCLTech, our teams bring together specialists in materials science, biomedical engineering, analytical chemistry, toxicology, microbiology, and veterinary sciences to interpret regulatory intent. This integrated scientific approach helps manufacturers strengthen compliance with standards like ISO 10993‑1:2025 while building more robust, future-ready biological safety programs.
This real-world case illustrates a broader trend across MedTech:regulatory change can become an opportunity to move from reactive updates to future-ready evidence systems. As standards continue to evolve, the companies that succeed are those that treat compliance as a matter of building more resilient, scientifically mature product development frameworks that reduce long-term risk and accelerate innovation; not a paperwork update.
How ISO 10993‑1:2025 will shape tomorrow’s compliance landscape
The upcoming ISO 10993‑1:2025 revision represents more than a routine update; it marks a strategic shift toward scientific, risk-based and ethically responsible biocompatibility evaluation. Expect stronger alignment with global standards and greater emphasis on real-world use conditions.
Risk-based approaches, supported by advanced in vitro and in silico testing, will be central to streamlining compliance and accelerating innovation. Biological evaluation plans should be redesigned to meet these new expectations while maintaining efficiency and scientific rigor.
Manufacturers who adopt these changes early will not only ensure compliance but also enhance device safety, simplify regulatory reviews and future-proof their product portfolio.
Next steps for manufacturers
- Revisit device categorization and identify documentation gaps
- Align biological evaluation with ISO 14971 risk management
- Incorporate lifecycle assessment and degradation testing
- Address new endpoints: genotoxicity, immunotoxicity, neurotoxicity
Learn more
Understanding ISO 10993-1:2025 is critical for staying ahead. Explore best practices and strategies to ensure compliance and protect your portfolio. Learn more about navigating regulatory changes: ISO 10993-1:2025 - Biological evaluation of medical devices — Part 1: Requirements and general principles for the evaluation of biological safety within a risk management process.

 Listen to article
Listen to article





