Enterprises today recognize data as a strategic priority. In a recent survey by Harvard Business Review, 33% of respondents defined themselves to be data-to-value leaders. However, the challenge lies in extracting the maximum value from their data, especially in the face of escalating complexity of their enterprise data and cloud environments. Moreover, 31% of respondents also said that data governance and management is one of the biggest challenges in managing multi-cloud environments. In this blog post, we will explore the benefits, challenges, and solutions for better data governance and management.
Cloud Migration and Data Governance
A data governance approach is a set of processes and procedures that enable organizations to manage their data in a secure and useful way throughout its life cycle, from acquisition to usage to disposal. It is important for the organization to consider the entirety of the data process chain which includes, data acquisition, analysis, insights generation, and deployment.
In fact, this entire process needs to adhere to the highest levels of governance across the organization to be truly effective. An effective data governance program integrates a central body or commission, a determined set of practices, and a plan to carry out those procedures. Therefore, it includes the means that people, processes, and technology could act together to facilitate auditable acquiescence with described and agreed-upon information policies.
Good data governance has several benefits. It can instigate customer trust and result in vast developments in user experience. However, with organizations rapidly moving to a cloud-based architecture, there are new data governance challenges. Since organizations generate and use data at extraordinary rates, the diversity of information and sources requires them to deal with information access, security, and control, governance, along with regulatory compliance.
The widespread implementation of cloud is now being obstructed by poor transparency and liability as it is no longer assured by means of any conventional security auditing techniques. Customers prefer cloud for its potential to scale rapidly based on business demand and lessen problems particularly IT overcapacity. Adapting the cloud has incredible benefits; however, it is considered a sizeable change. Moreover, the traditional change management process in cloud has its own set of challenges as well. This is where Google Cloud can assist organizations to move, and subsequently govern, their data with security and efficiency.
Achieving Data Assurance with Google Cloud Platform
Moving workloads to the Google Cloud Platform requires adherence to the structure that controls all the cloud resources and the respective strategies for each product. Every resource in Google Cloud is generally systematized in a hierarchy. Since the dynamics of data management alter in many fundamental ways when a business creates and stores more information in the cloud, risk management and privacy must be considered.
Accordingly, the data access layer in the Google Cloud platform is set up based on data sensitivity and privacy. It also provides a well-defined change management process and communication to all stakeholders to simplify the large change. Data quality expectations, systems, and performance are recorded which assist the data justification and monitoring process.
As implementation rates of Google Cloud continue to skyrocket, queries about potential stakes of dealing with data in the cloud also emerge for many reasons, such as protecting and securing the information, regulations, visibility and management. These risk factors emphasize the need for better data assessment, classification of metadata, data quality, and information security as fundamental data governance components.
Different data customers have different quality requirements, making it significant to record expectations, techniques, and tools for contributing to data substantiation and monitoring. These data quality management methods provide essential features, such as control validation, empowering quality monitoring and reporting, supporting triage process, solution recommendation, and data tracking. The right practices for data quality management provide noticeably reliable data for further analysis.
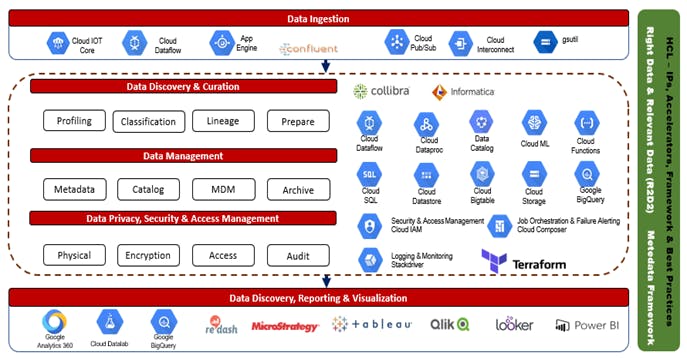
Figure 1: Sample illustration of HCLTech Data Governance framework on Google Cloud
The HCLTech Google Business Unit has successfully implemented their Data Governance framework for many customers. Here are the highlights from one of the implementations for a leading European Financial Institute built on people, process, and technology.
- Aligned leadership across business data owners, business data consumers, and IT data and identified stewards for data sources on the IT side with full accountability
- Established processes to route the security requests
- Established data quality and availability expectations and streamlined data request process
- Executed tool-based monitoring of data access and the metadata repository
- Provided regular data usage reports
- Optimized resources based on usage
- Automated consolidation of metadata from various sources– data models/databases, business definitions and rules, ETL, BI, etc.
- Implemented data lineage and impact analysis capabilities
Cloud monitoring identifies and monitors cloud resources continuously and the process takes place automatically on Google Cloud. The service generally integrates default dashboards for various Google cloud platform out-of-the-box and integrates metrics and critical metadata. This makes it simple to comprehend the relations among components and examine auto-scaling clusters.
The Google Cloud platform counters issues around compliance, cost, and loss of control by offering users remarkable control over every instance running on Google’s system. The responsibility for the security management on the user’s operating system or applications on Google Cloud falls on the user. It’s only by adhering to the necessary best practices of data security can both operating systems and applications be assured. The paradigm orchestrates a shared responsibility between customers and Google accordance with the prescribed data security standard as per a qualified security assessor.
Key Considerations for Building a Google Cloud Data Governance Practice
As more organizations link their data resources to Google Cloud, the demand for auditable systems for assuring data service will continue to emerge. To deal with these directives, it is important for organizations to frame their data governance practices based on certain components including:
- A framework that empowers people to classify, embark on, and implement data policies
- Effective systems for control, error, and stewardship over every data resource across on-premises systems and storage on the cloud
- The right tools and technologies for engaging data policy compliance
Evolving with Google Cloud
Google Cloud’s approach towards data security and acquiescence is inclusive and ethical, which organizations can rely on to increase the usage of the Google Cloud beyond a BigQuery service. A successful data governance policy paves the way for organizations to institute control and retain visibility into their data resources, creating a competitive edge over their peers. It also generates immense business value by instituting a data-driven practice that further enables them to improve decision-making, manage risks better, and stay on top of regulatory compliances.


