Overview
Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS), often referred to as ’Forever Chemicals’, comprise a diverse group of more than 10,000 synthetic chemicals. First developed in the mid-20th century, PFAS quickly gained popularity due to their exceptional durability and resistance properties, making them valuable across consumer goods and industrial products. However, their widespread use has now raised significant environmental and health concerns.
Since the 1950s, PFAS have been widely used for their water- and oil-repellency, heat resistance and durability. Today, the contamination of water systems by PFAS has become a primary public concern. Research has linked PFAS exposure to a range of adverse effects, including cancers, hormone disruption and immune system impairments. Their persistence in the environment and the human body makes them challenging to remove, heightening concerns about their widespread presence.
Challenges for MedTech companies
The medical device industry faces mounting pressure due to increasing scrutiny and evolving regulations concerning Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) use. These regulations are driven by the environmental persistence and potential health risks associated with PFAS, which are widely used in various industrial applications, including medical devices.
- Regulatory compliance by 2027: Regulatory bodies are expected to enforce non-PFAS compliance by 2027, prompting MedTech companies to adapt swiftly to these changes. This involves ensuring their products are free from PFAS while maintaining safety and performance standards.
- R&D challenges in identifying and replacing PFAS: Companies must first pinpoint PFAS usage in medical devices and supplies, then find suitable alternatives that possess the same properties, such as water and oil resistance, heat resistance and durability, without compromising the functionality and performance of the medical devices. Developing these alternatives requires substantial investment in research, innovative materials and thorough testing to ensure efficacy and safety.
- Material compatibility: Ensuring that PFAS-free alternatives are compatible with existing manufacturing processes and medical device designs.
- Performance standards: Maintaining the performance standards of medical devices while switching to PFAS-free materials, ensuring they meet the necessary safety and efficacy requirements.
- Cost implications: Transitioning to PFAS-free materials may involve significant costs, including research, testing and product requalification.
- Supply chain disruptions: Identifying and sourcing PFAS-free materials may disrupt established supply chains and require the development of new vendor relationships.
Solutions
- Conduct product portfolio assessments: Identify PFAS presence across the product range, including components and associated materials.
- Supply chain analysis: Conduct end- to-end evaluations to identify PFAS use in raw materials and manufacturing processes.
- Collaborate with vendors and suppliers: Work together to find sustainable, PFAS-free alternatives that maintain the functionality and performance of medical devices.
- Research and development: Engage in research to develop new materials that meet necessary performance standards without relying on PFAS. This includes exploring bio-based alternatives or fluorine-free technologies.
- Compliance with global regulations: Ensure the transition to PFAS-free alternatives aligns with global regulatory frameworks and safety standards.
Impact
PFAS regulations significantly impact medical device manufacturers, affecting financial costs, operational adjustments and market dynamics.
- Monetary impact: Compliance requires substantial investments in material substitution, process reengineering, testing and certification. Non-compliance can lead to hefty fines and legal costs. Material substitution, process reengineering, ongoing testing and certification can be very expensive. Non-compliance fines can be substantial, with additional legal costs. Complying with international PFAS regulations can be financially demanding.
- Operational impact: Adjusting supply chain adjustments may increase procurement costs. Re-engineering production processes can cause temporary production delays and inefficiencies. Enhanced regulatory scrutiny requires meticulous documentation and reporting, increasing administrative costs.
- Market dynamics: Companies that proactively address PFAS regulations can gain a competitive edge by demonstrating their commitment to safety and sustainability. Regulations drive innovation, leading to the development of PFAS-free alternatives and opening new market opportunities. Compliance with PFAS regulations can bolster consumer trust, positively impacting sales and brand loyalty.
- Long-term strategic impact: Proactively reducing PFAS aligns with broader sustainability goals and corporate social responsibility initiatives, enhancing a company's CSR profile and attracting investors and stakeholders.
Navigating these challenges requires a comprehensive approach, including collaboration across departments, investment in research and development and proactive engagement with regulatory bodies to ensure compliance and minimize disruptions to the supply chain.
How can HCLTech help?
At HCLTech, we have a long history of leading the removal of potentially harmful substances from MedTech products, which goes beyond what is required for regulatory compliance.
Our experts
- Polymer and material science
- Biomedical engineering
- Organic and analytical chemistry
- Veterinary sciences
- Pharmacology and toxicology
- Biotechnology and microbiology
As part of this effort, we are currently engaging with all our customers to phase out PFAS by proactively identifying and developing PFAS-free sustainable alternatives without compromising the function and performance of the devices. Below are the accelerators, tools, software, ecosystem for PFAS assessment and remediation.
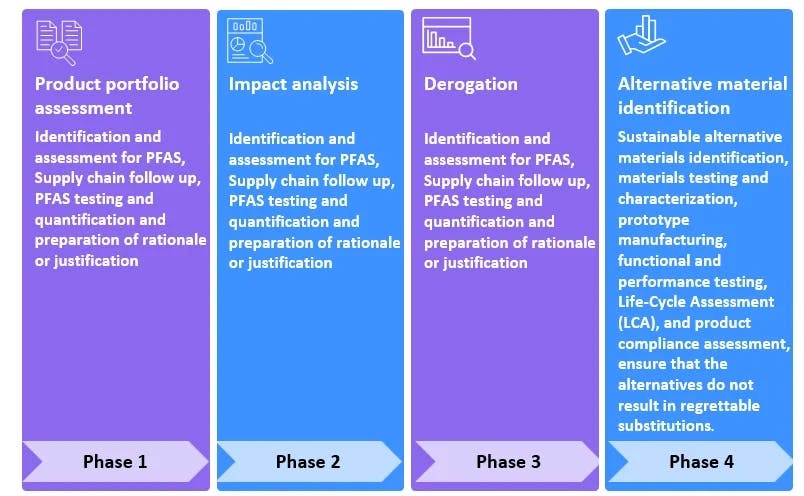
PFAS – Assessment Compliance Execution Flow
- Familiarize the manufacturers with various PFAS regulations across the globe.
- Conduct a product portfolio assessment and an impact analysis for the presence of PFAS.
- Identify PFAS in the supply chain.
- Prepare comprehensive plans to eliminate PFAS from raw materials and manufacturing processes
- Collaborate with vendors or supply chains early and identify a suitable material to meet the reporting requirements
- Conduct research to identify potential sustainable alternatives to PFAS

AI/ GenAI for PFAS assessment and alternate material identification
At HCLTech, we are integrating GenAI with every stage of our PFAS remediation process. Our state-of-the-art technology has the ability to integrate with a wide range of PLM tools, break down products to their raw materials, analyze for any potential PFAS compounds from the manufacturing to the raw material level, co-relate with PFAS regulations around the world and identify the potential components/ products/ compounds which are at risk due to the upcoming regulations. Furthermore, it helps us with mapping and timeline automation, providing a detailed view of when and what type of remediation must be taken at each level (product/ component/ raw material). We are also looking at integrating PFAS test reports and identifying potential alternatives.



